Last November 15 I participated in the postgraduate symposium of the Warburg Institute Mnemonic Waves, with a paper on caricatures and the post-Warburgian studies titled Caricatures as Pathosformeln. Gombrich, Warburg, and the Emotions, of which I publish here the text.
Tag Archives: Leonardo da Vinci
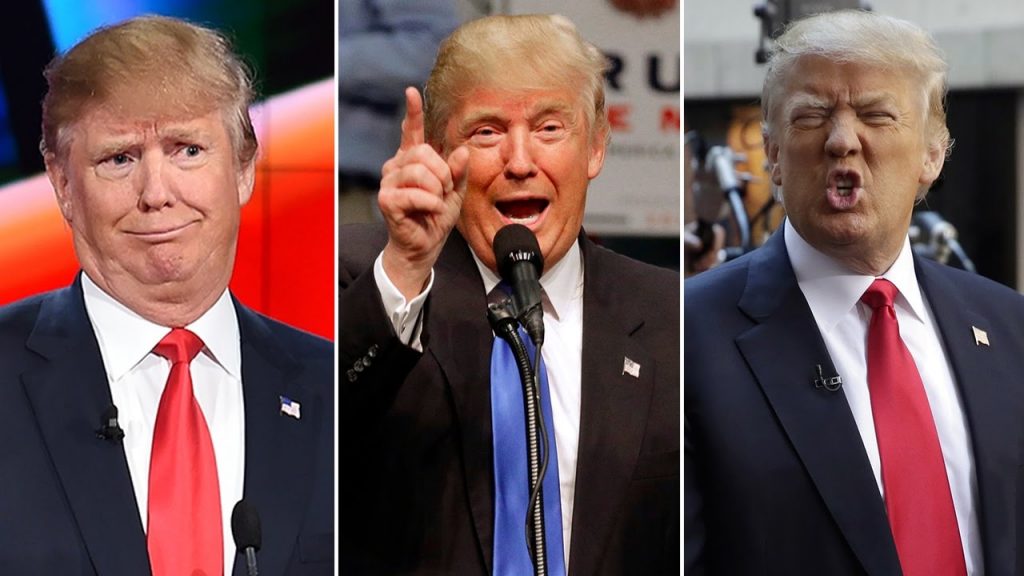
Caricature as emotional knowledge
I publish here the talk I’ve given at the Mis-Shapings conference last September 13 at Queen Mary University.
Do we believe in physiognomy? Do we believe, as the Italian anthropologist Cesare Lombroso did, that psychological, emotional, moral attitudes of the individuals can be divined by observing the shape and features of the face?
No, of course we don’t. Physiognomy is pseudo-science, dismissed knowledge, superstition. We can’t make assumptions merely relying on appearances. Can we?
Actually, we do. We do it in our daily life, often unintentionally. But even when we look at artworks we allow us to believe in physiognomy. Continue reading
Leonardo: the first caricaturist
While reaching an outstanding complexity in the improvement of the human portrait, while exploring the perfection of the human body’s proportions and symmetries, Leonardo da Vinci sketches several experiments in deformation and exaggeration of the human figure.
- Leonardo Da Vinci, Lady With an Ermine, 1489-1490, Cracow, Czartoryski Museum. Source: Wikimedia Commons, public domain.
- Leonardo da Vinci, Vitruvian Man, Venice, Galleria dell’Accademia, Gabinetto dei disegni e delle stampe. Source: Wikimedia Commons, public domain.
- Wenceslaus Hollar, Two Deformed Heads after Leonardo,1645. Source: Wikimedia Commons, public domain.
Scholars refer to Leonardo’s deformations as proto-caricatures, because of their lack of explicit satirical aims. Indeed, Leonardo’s misshapen figures are entangled with his more general inquiry on the human subject, on the inherent shape, both physical and psychological, of the human individual. In this perspective, the caricature can be considered as the exploration of divergent possibilities of representation of humanness, and also a form of criticism against the canonization of the Renaissance portrait, that adopted idealized models screening off the observation of reality.