Last November 15 I participated in the postgraduate symposium of the Warburg Institute Mnemonic Waves, with a paper on caricatures and the post-Warburgian studies titled Caricatures as Pathosformeln. Gombrich, Warburg, and the Emotions, of which I publish here the text.
Tag Archives: Mussolini
Caricature as emotional knowledge
I publish here the talk I’ve given at the Mis-Shapings conference last September 13 at Queen Mary University.
Do we believe in physiognomy? Do we believe, as the Italian anthropologist Cesare Lombroso did, that psychological, emotional, moral attitudes of the individuals can be divined by observing the shape and features of the face?
No, of course we don’t. Physiognomy is pseudo-science, dismissed knowledge, superstition. We can’t make assumptions merely relying on appearances. Can we?
Actually, we do. We do it in our daily life, often unintentionally. But even when we look at artworks we allow us to believe in physiognomy. Continue reading
Mis-Shapings: abstracts
Here are brief descriptions of the papers that will be presented next September 13th at the Mis-Shapings conference.
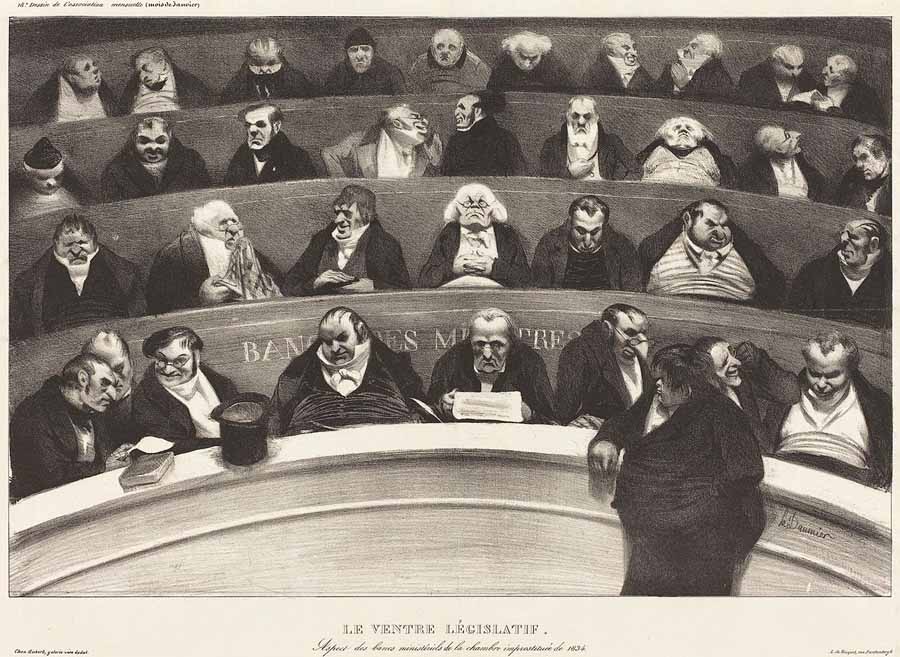

Honoré Daumier, Le ventre législatif, 1834
Socialising anger. Fascism and emotions
Last June 22nd I participated in the Literature and Social Emotions Conference at the University of Bristol. I presented a paper titled Socialising Anger. Literary Representations of Emotional Communities under Fascism, which is a development of the research I first presented one year ago and will result in a broader scrutiny on the representation of emotions in fascism-related Italian literature. What follows is the text of the Bristol’s paper.
1.
Italian fascism pursued strict management of public feelings. It aimed at a wide and deep control of human thoughts and experiences. That is to say, it built what William Reddy defines an ‘emotional regime’; it established a set of practices which inculcated normative emotions, like enthusiasm, exaggerated optimism, national pride. Nevertheless, the euphoric feelings displayed in public represent just one of the emotional layers of fascist Italy. Despite the appearance of unanimous acceptance, fascism largely derived consensus from violence and intimidation. As denounced by Carlo Emilio Gadda in the very first lines of his anti-fascist satire Eros e Priapo, written in 1944-1945.
Collective and individual consciousness, threatened by the knife, the truncheon, the torture; and silenced by prisons, extorsions, vetos against free expression; it was concealed in a hidden, invisible lagoon of history, beyond hate and dullness, and belonged to the refugees, the persecuted, the prisoners, the humiliated, children of deportees and executed to death.
Along with material and physical coercion, fascism caused the emotional suffering of part of the population. Gadda sketches the existence of what Reddy would call an ‘emotional refuge’, a cluster of social conditions and related practices diverging from the emotional regime.

Anger as misshapen fear: fascism and the emotional body
What follows is the text of the paper I gave the 20 June 2017 at the International Conference «Fears and Angers. Historical and Contemporary Perspectives», Queen Mary University, 19-20 June 2017.
Probably Federico Fellini’s Oscar-winning movie, Amarcord, released in 1973, perfectly defines what was supposed to be the, as William Reddy would say, «emotional regime» of fascism. Enthusiasm, faith, happiness, and veneration for the Chief were the dominant public feelings endorsed by fascism. But, despite the public ceremonies being widely, and often sincerely, officiated by Italian people, fascism largely derived consensus from violence and intimidation.

Giacomo Manzù, Black Brigadist, 1943
The cognition of Priapus. Gadda and caricature
Is out my last essay, The Cognition of Priapus. Caricature procedures in Carlo Emilio Gadda’s Eros e Priapo. Here it is available the English abstract, while here you can find the whole essay in Italian.
I extract from the essay three different caricatural descriptions of Benito Mussolini provided by Gadda in his controversial pamphlet Eros e Priapo, written between 1944 and 1945. In the first, Gadda portraits the image of Mussolini speaking from the sadly well-known balcony:
Di colassù i berci, i grugniti, i sussulti priapeschi, lo strabuzzar d’occhî e le levate di ceffo d’una tracotanza priapesca: dopo la esibizione del dittatorio mento e del ventre, dopo lo sporgimento di quel suo prolassato e incinturato ventrone, dopo il dondolamento, in sui tacchi, e ginocchî, di quel culone suo goffo e inappetibile a chicchessia, ecco ecco ecco eja eja eja il glorioso, il virile manustupro: e la consecutiva maschia polluzione alla facciazza del «pòppolo».